William L. Allen, Associate Editor
Gender differences in academic publications: why it matters
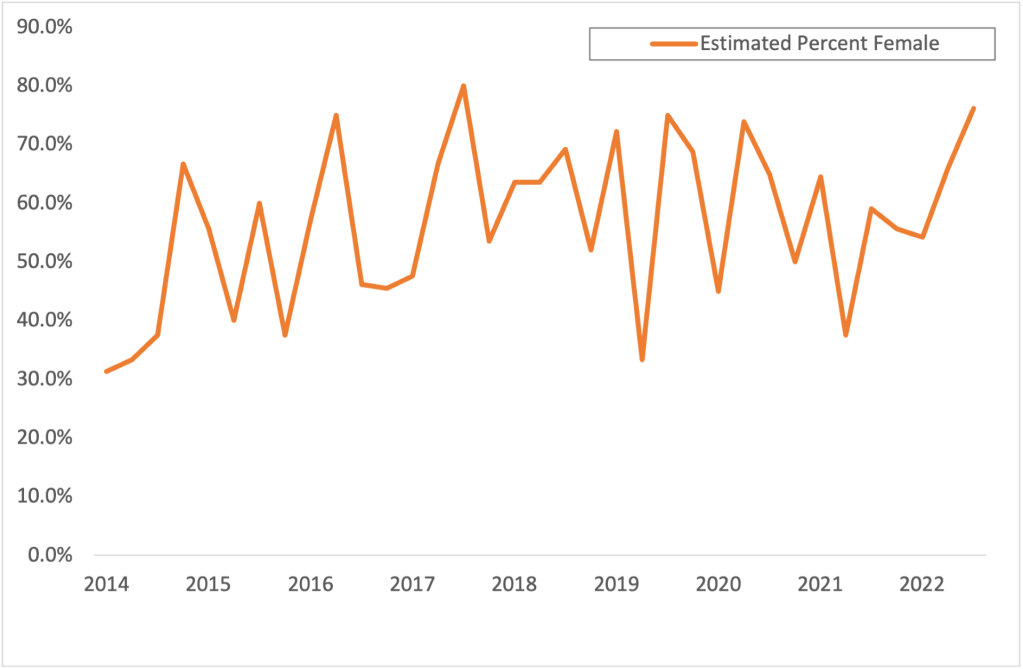
Across fields, there are concerns about the extent to which gender disparities exist in academic journal publications. Several studies of professional social science—including in economics, political science, and sociology—indicate women remain underrepresented in the pages of top journals. Inequalities in this regard may be particularly consequential because peer-reviewed publications remain one of the most important factors that contribute to success in applications for academic jobs, promotions, and grants.
While there are several reasons for this pattern, including authors’ perceptions of where their kinds of work are more likely to be favorably received, the simple fact of its presence has been enough motivation for some journal editorial teams to explicitly measure and report on the gender breakdown of both submissions and published work where possible.
Continue reading